Hough Transform 코드 분석
Hough Transform
Hough transform이란
\[y=ax+b ↔ r=acos\theta + bsin\theta\]다음과 같이 직선의 방정식을 r과 θ 로 나타내는 것부터 시작한다.
직교좌표계에서는 수직선일 경우 기울기가 무한대여서 표현하기 적합하지 않기 때문에,
영상의 에지 점들을 극 좌표계로 옮겨 r 과 θ 로 직선을 표현한다.

그림1

그림2
그림 1의 a1,a2,a3를 지나는 모든 직선을 극좌표계로 표현하면 그림 2와 같이 된다.
즉, 그림2의 a1 곡선은 a1을 지나면서 θ=0인 직선부터, θ=π인 직선까지 극 좌표계로 표현한 그래프인 것이다.
그렇다면 저 세 곡선이 만나는 점은 무엇을 의미할까를 생각해보면,
점 a1을 지나면서 거리가 r, 각도가 θ인 직선,
=점 a2를 지나면서 거리가 r, 각도가 θ인 직선,
=점 a3를 지나면서 거리가 r, 각도가 θ인 직선
인 것이다.

그림3
a1에서 θ를 증가시키면서 직선을 관찰하다 보면, 그 직선이 a2, a3를 지날 때가 있을 것이다.
a2,a3도 마찬가지이다. 그 때의 직선의 r과 θ는 모두 같을 것이다.
그렇기 때문에 r,θ 그래프에서 한 점에서 만나는 것이다.
그림4
점 3개를 예로 들어 극좌표계에 표시해보면, 그림4와 같다.
각도가 0부터 $\pi$까지 증가하면서 해당하는 (r,θ) 좌표값을 1 증가시킨다.
그러면 a1,a2,a3를 지나는 직선에 해당하는 누적된 좌표값은 3이 될 것이다.
이 누적된 값이 가장 큰 좌표가 가장 긴 직선이라 할 수 있겠다.
이렇게 누적된 값을 이용하여 직선을 추출하는 데 이용하는 것이다.
이미지로 적용
자 이제 x,y 그래프의 1사분면을 image 공간이라고 생각해보자.
각 점들은 이미지의 픽셀을 의미한다.
단계는 다음과 같다.
-
각 픽셀마다 θ=0인 직선부터, θ=π인 직선을 돌며 극좌표계 행렬에 표시
- 직선이 겹치지 않도록 local maximum값 선정
- 임계값 이상의 누적 좌표값 선별
- 직선을 누적값 기준으로 내림차순 정렬
허프 변환 좌표계를 위한 행렬
$-\rho_{max}\leq \rho\leq \rho_{max}$ , $\rho_{max} = height + width, acc_h = (\rho_{max}*2)/\Delta\rho$
$0\leq \theta\leq\theta_{max}, \theta_{max}=\pi, acc_\omega=\pi/\Delta\theta$
(근데 왜 $\rho_{max} = height + width$ 인지 모르겠다..)
void hough_coord(Mat image, Mat& acc_mat, double rho, double theta)
{
int acc_h = int((image.rows + image.cols) * 2 / rho);
int acc_w = int(CV_PI / theta);
acc_mat = Mat(acc_h, acc_w, CV_32S, Scalar(0));
for (int i = 0; i < image.rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < image.cols; j++)
{
Point pt(j, i);
if (image.at<uchar>(pt) > 0) {
for (int t = 0; t < acc_w; t++)
{
double radian = t * theta;
double r = pt.x * cos(radian) + pt.y * sin(radian);
r = cvRound(r / rho + acc_mat.rows / 2.0);
acc_mat.at<int>( (int)r, t)++;
}
}
}
}
}
image 픽셀이 0보다 크면, 그 점에서 각도를 $\pi$까지 증가시키며 acc_mat 행렬에 그 때의 (r, θ) 좌표값을 1 증가시킨다. canny edge 함수로 edge만 뽑아낸 image를 활용하기 때문에 연산량이 생각보다 많지 않을것이다. acc_mat 행렬에 넣을 때는 r값이 마이너스인 경우를 고려하여 acc_mat.rows/2를 더해준다.
Local maximum 추출
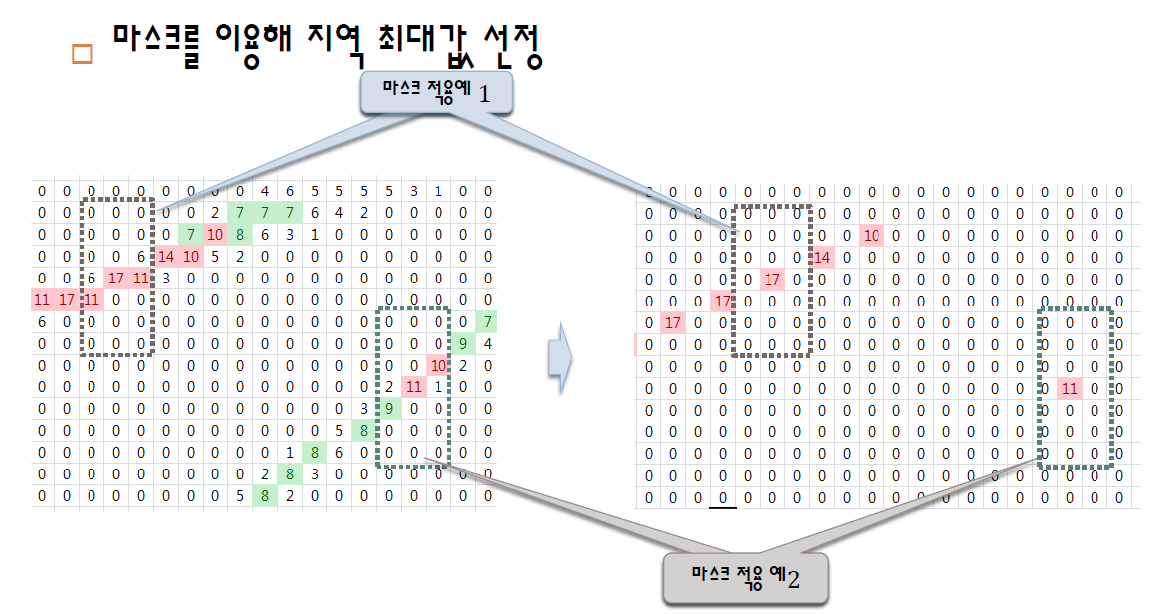
그림5
그림5와 같이 3x7 사이즈의 마스크를 이용하여 그 마스크의 중앙값이 최대일 경우 그 값만 빼고 나머지는 0으로 만드는 과정이다.
void acc_mask(Mat acc_mat, Mat& acc_dst, Size size, int thresh)
{
acc_dst = Mat(acc_mat.size(), CV_32S, Scalar(0));
Point h_m = size / 2; // 마스크 크기 절반
for (int r = h_m.y; r < acc_mat.rows - h_m.y; r++) {
for (int t = h_m.x; t < acc_mat.cols - h_m.x; t++)
{
Point center = Point(t, r) - h_m;
int c_value = acc_mat.at<int>(center); // 중심화소
if (c_value >= thresh)
{
double maxVal = 0;
for (int u = 0; u < size.height; u++) {
for (int v = 0; v < size.width; v++)
{
Point start = center + Point(v, u);
if (start != center && acc_mat.at<int>(start) > maxVal)
maxVal = acc_mat.at<int>(start);
}
}
Rect rect(center, size);
if (c_value >= maxVal)
{
acc_dst.at<int>(center) = c_value;
acc_mat(rect).setTo(0);
}
}
}
}
}
acc_mat 행렬에서 마스크를 돌면서 maxVal을 찾고, center 값이 maxVal보다 크면 acc_dst의 행렬에 center값을 넣고 acc_mat행렬에 해당 마스크 안의 좌표값을 다 0으로 만든다. 이것을 반복하면 그림5의 두번째 그림처럼 직선이 겹치지 않게 local maximum을 추출할 수 있다.
Line 그리기
void thres_lines(Mat acc_dst, Mat& lines, double _rho, double theta, int thresh)
{
for (int r = 0; r < acc_dst.rows; r++) {
for (int t = 0; t < acc_dst.cols; t++)
{
float value = (float)acc_dst.at<int>(r, t); // 누적값
if (value >= thresh) // 직선 길이 임계값
{
float rho = (float)((r - acc_dst.rows / 2) * _rho); // 수직거리
float radian = (float)(t * theta); // 각도
Matx13f line(rho, radian, value); // 단일 직선
lines.push_back((Mat)line);
}
}
}
}
Line을 그리기 위해 threshold값 이상의 누적값을 가진 좌표값들을 line이라는 1*3 행렬에 저장한 후 다시 lines라는 행렬에 (r,θ,value) 행렬을 넣어준다. 나중에 value가 큰 순서부터 정렬하기 위해서이다.
lines 행렬 정렬
void sort_lines(Mat lines, vector<Vec2f>& s_lines )
{
Mat acc = lines.col(2), idx;
sortIdx(acc, idx, SORT_EVERY_COLUMN + SORT_DESCENDING);
for (int i = 0; i < idx.rows; i++)
{
int id = idx.at<int>(i);
float rho = lines.at<float>(id, 0); // 수직거리
float radian = lines.at<float>(id, 1);
s_lines.push_back( Vec2f(rho,radian));
}
}
lines 행렬의 2번째 값인 value(누적값)을 기준으로 내림차순 정렬하는 과정이다.
idx 행렬에 value 값이 큰 순서부터 들어간다.
그 후, s_lines 벡터에 (r,θ) 벡터를 넣어 허프라인을 그릴 벡터를 생성한다.
houghLines
void houghLines(Mat src, vector<Vec2f>& s_lines, double rho, double theta, int thresh)
{
Mat acc_mat, acc_dst, lines;
hough_coord(src, acc_mat, rho, theta);
acc_mask(acc_mat, acc_dst, Size(3, 7), thresh);
thres_lines(acc_dst, lines, rho, theta, thresh);
sort_lines(lines, s_lines);
}
위의 함수들을 한 함수에 정리한 것이다.
허프라인 그리기
void draw_houghLines(Mat image, Mat& dst, vector<Vec2f> lines, int nline)
{
if (image.channels() == 3) image.copyTo(dst);
else cvtColor(image, dst, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < min((int)lines.size(), nline); i++)
{
float rho = lines[i][0], theta = lines[i][1];
double a = cos(theta), b = sin(theta);
Point2d delta(1000 * -b, 1000 * a);
Point2d pt(a*rho, b*rho);
line(dst, pt + delta, pt - delta, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1, LINE_AA);
}
}
min((int)lines.size(),nline)은 최대 nline 값만큼만 line을 그리겠다는 것이다. lines 벡터는
dst 행렬에 pt+delta 포인트부터 pt-delta까지 그리는데, 왜 그런지 한번 생각해보았다.

그림6
위 그림과 같이 pt에서 1000픽셀만큼 떨어진 A1, A2 점을 잡아 라인을 그리겠다는 것이다.
전체 코드
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void hough_coord(Mat image, Mat& acc_mat, double rho, double theta)
{
int acc_h = int((image.rows + image.cols) * 2 / rho);
int acc_w = int(CV_PI / theta);
acc_mat = Mat(acc_h, acc_w, CV_32S, Scalar(0));
for (int i = 0; i < image.rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < image.cols; j++)
{
Point pt(j, i);
if (image.at<uchar>(pt) > 0) {
for (int t = 0; t < acc_w; t++)
{
double radian = t * theta;
double r = pt.x * cos(radian) + pt.y * sin(radian);
r = cvRound(r / rho + acc_mat.rows / 2.0);
acc_mat.at<int>( (int)r, t)++;
}
}
}
}
}
void acc_mask(Mat acc_mat, Mat& acc_dst, Size size, int thresh)
{
acc_dst = Mat(acc_mat.size(), CV_32S, Scalar(0));
Point h_m = size / 2; // 마스크 크기 절반
for (int r = h_m.y; r < acc_mat.rows - h_m.y; r++) {
for (int t = h_m.x; t < acc_mat.cols - h_m.x; t++)
{
Point center = Point(t, r) - h_m;
int c_value = acc_mat.at<int>(center); // 중심화소
if (c_value >= thresh)
{
double maxVal = 0;
for (int u = 0; u < size.height; u++) {
for (int v = 0; v < size.width; v++)
{
Point start = center + Point(v, u);
if (start != center && acc_mat.at<int>(start) > maxVal)
maxVal = acc_mat.at<int>(start);
}
}
Rect rect(center, size);
if (c_value >= maxVal)
{
acc_dst.at<int>(center) = c_value;
acc_mat(rect).setTo(0);
}
}
}
}
}
void thres_lines(Mat acc_dst, Mat& lines, double _rho, double theta, int thresh)
{
for (int r = 0; r < acc_dst.rows; r++) {
for (int t = 0; t < acc_dst.cols; t++)
{
float value = (float)acc_dst.at<int>(r, t); // 누적값
if (value >= thresh) // 직선 길이 임계값
{
float rho = (float)((r - acc_dst.rows / 2) * _rho); // 수직거리
float radian = (float)(t * theta); // 각도
Matx13f line(rho, radian, value); // 단일 직선
lines.push_back((Mat)line);
}
}
}
}
void sort_lines(Mat lines, vector<Vec2f>& s_lines )
{
Mat acc = lines.col(2), idx;
sortIdx(acc, idx, SORT_EVERY_COLUMN + SORT_DESCENDING);
for (int i = 0; i < idx.rows; i++)
{
int id = idx.at<int>(i);
float rho = lines.at<float>(id, 0); // 수직거리
float radian = lines.at<float>(id, 1);
s_lines.push_back( Vec2f(rho,radian));
}
}
void houghLines(Mat src, vector<Vec2f>& s_lines, double rho, double theta, int thresh)
{
Mat acc_mat, acc_dst, lines;
hough_coord(src, acc_mat, rho, theta);
acc_mask(acc_mat, acc_dst, Size(3, 7), thresh);
thres_lines(acc_dst, lines, rho, theta, thresh);
sort_lines(lines, s_lines);
}
void draw_houghLines(Mat image, Mat& dst, vector<Vec2f> lines, int nline)
{
if (image.channels() == 3) image.copyTo(dst);
else cvtColor(image, dst, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < min((int)lines.size(), nline); i++)
{
float rho = lines[i][0], theta = lines[i][1];
double a = cos(theta), b = sin(theta);
Point2d delta(1000 * -b, 1000 * a);
Point2d pt(a*rho, b*rho);
line(dst, pt + delta, pt - delta, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1, LINE_AA);
}
}
int main()
{
Mat image = imread("../image/hough_test.jpg", 0);
CV_Assert(image.data);
Mat canny, dst1, dst2;
GaussianBlur(image, canny, Size(5, 5), 2, 2);
Canny(canny, canny, 100, 150, 3);
double rho = 1, theta = CV_PI / 180;
vector<Vec2f> lines1, lines2;
houghLines(canny, lines1, rho, theta, 50);
HoughLines(canny, lines2, rho, theta, 50);
draw_houghLines(canny, dst1, lines1, 10);
draw_houghLines(canny, dst2, lines2, 10);
imshow("source", image);
imshow("canny", canny);
imshow("detected lines", dst1);
imshow("detected lines_OpenCV", dst2);
waitKey();
}
결과물

그림 7 원본,canny edge, hough lines
